Discover the essence of innovation through condensed stories of China’s top companies. Dive into our ‘Unleashing Innovation in China’ series to get inspired and see innovation in action. We distill insights from digital transformation and market expansion leaders, offering a fresh look at how these brands navigate and shape global business landscapes.
NIO’s Journey: From Start-up to Premium EV Pioneer
Founded in 2014, NIO has rapidly emerged as one of China’s leading electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers. With its “Internet mindset,” and premium brand positioning, NIO has differentiated itself from competitors in China’s fiercely competitive EV market.

Early Milestones: Brand-Building Before Production
NIO’s emphasis on brand recognition started early. Its foray into motorsports — winning the 2015 Formula E Championship in 2015, established its name well before mass production. In 2016, NIO unveiled the EP9, a luxury supercar, priced at USD 1.48 million and marketed exclusively to elite investors, including Tencent’s Pony Ma. The EP9 set a world record for EVs, reinforcing NIO’s premium image.
This was followed by the launch of NIO’s first mass-market SUV, the ES8, in 2017, which helped the company break into the mid-to-high-end EV segment.
Global Ambitions: Research, Design, and Expansion
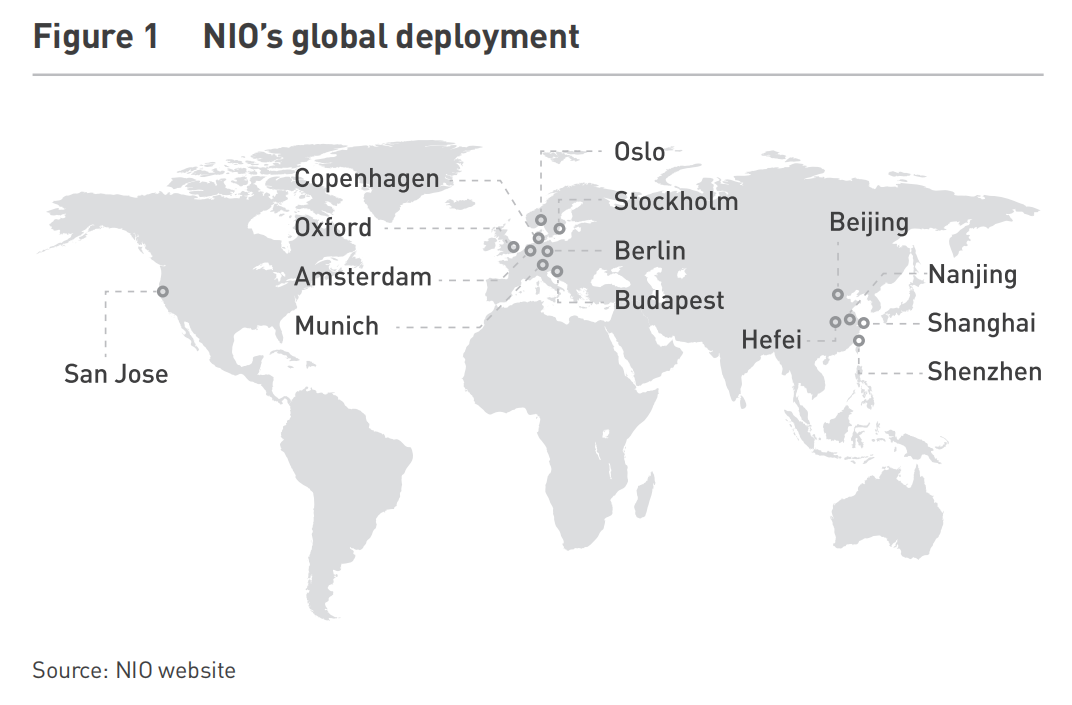
NIO has built a global network of research and development (R&D) centers (see Figure 1). Key locations include Shanghai for production models, Beijing for software, San Jose for intelligent driving and Oxford for advanced engineering. Meanwhile, its global design hub in Munich reflects NIO’s aspiration to align with global luxury standards.
NIO’s physical footprint also extends to overseas markets. In cities like Oslo, NIO Houses —its customer experience centers—offering a full-service ecosystem, combining sales, events, and community engagement.
Strategic Partnerships and Growth
The company owes much of its rapid ascent to founder and Chairman, William Li, dubbed the “godfather of the transport sector” in China. Li, who previously co-founded Beijing Bitauto Holdings, brought together early investors such as Tencent, Baidu, Hillhouse Capital, and Sequoia Capital. He also assembled a seasoned leadership team comprising former executives from Tesla, BMW, Volkswagen, and General Motors.
NIO’s IPO on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in September 2018 marked a turning point. The company raised USD 1 billion, achieving a market capitalization of over USD 6 billion. While its stock initially faced skepticism, shares rebounded dramatically in 2020, with NIO’s market value surpassing USD 100 billion—a testament to its investor confidence and growth trajectory.
Core Competitiveness: Technology and Services
NIO’s success rests on three strategic pillars: cost-effective production, advanced technology, and premium customer service.
1. Outsourced Production: NIO’s cost-efficient production model leverages its partnership with JAC Motors. Rather than investing in costly manufacturing facilities, NIO focuses on quality control, R&D, and inspections while JAC owns and operates the production plants. By 2022, this collaboration enabled NIO to produce 100,000 vehicles. Although NIO considered in-house production, it opted to deepen its partnership with JAC, forming a joint venture in 2021.
2. Cutting-Edge Technology: NIO’s prioritizes innovation across software and autonomous driving. Its in-car operating system, “NOMI” OS, powered by cloud computing, enables voice command functionality for enhanced user experience. NIO’s Aquila Super Sensing system combines LiDAR and camera technology, surpassing competitors like Xpeng and Tesla with 33 sensors for optimal performance. Meanwhile, its NIO Adam supercomputer, featuring four NVIDIA Orin chips, delivers 1,000 TOPS of processing power for advanced driving automation.
3. Premium Customer Service: NIO’s direct sales model eliminates intermediaries, offering customers seamless online and in-store experience. Post-purchase services, such as charging, maintenance and repair, ensure customer satisfaction. NIO Houses, positioned in first-tier cities, serve as community spaces offering amenities and events, fostering brand loyalty. By 2022, NIO has built over 1,300 battery-swapping stations and 13,000 charging piles, many at reduced or no cost to customers.
Challenges: Profitability and Competition
Despite stable deliveries in 2022 amid the COVID-19 pandemic, NIO faces challenges in achieving profitability and sustaining its competitive edge. Revenue reached RMB 49.27 billion (USD 7.3 billion), a 36% year-on-year increase, but net loss widened to RMB 14.44 billion (USD 2.2 billion). Although NIO maintains substantial cash reserves of RMB 23.04 billion, reducing operational costs and enhancing production are critical to achieving sustainable growth.
Competition is intensifying, both domestically and globally. NIO faces mounting pressure from established players like BYD and Tesla, which lead in production capacity, cost-efficiency, and technology. NIO’s premium customer services, such as its “butler-style” customer care, have built a loyal user base. However, these services incur high operating costs, (with flagship NIO Houses alone costing around RMB 100 million annually) posing a long-term challenge as sales volumes scale.
Safety concerns following serious road incidents have impacted NIO’s reputation, underscoring the need for further technological enhancements.

Future Prospects: Global Expansion and Market Positioning
NIO views traditional luxury automakers like BMW, Audi, and Mercedes as its primary competitors. With models like the ET7, NIO aims to solidify its premium segment position. However, Tesla’s dominance in production scale and affordability remains a formidable barrier.
Looking beyond China, NIO’s entry into Europe signals its ambition to become a global player. Plans to expand into the U.S. and other competitive markets will require significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and brand recognition. There is no doubt, to achieve success and profitability on the global stage, NIO will need to invest considerable effort and resources.
This article is originally published on: Unleashing Innovation: Ten Cases from China on Digital Strategy and Market Expansion – CKGSB Knowledge




















