From record-breaking online shopping festivals to supply chain transformations, Alibaba and JD.com have long shaped China’s e-commerce landscape. As these tech giants continue to evolve, their rivalry highlights distinct business models and innovations that drive their growth.
The Flywheel Effect: Two Approaches to E-Commerce Success
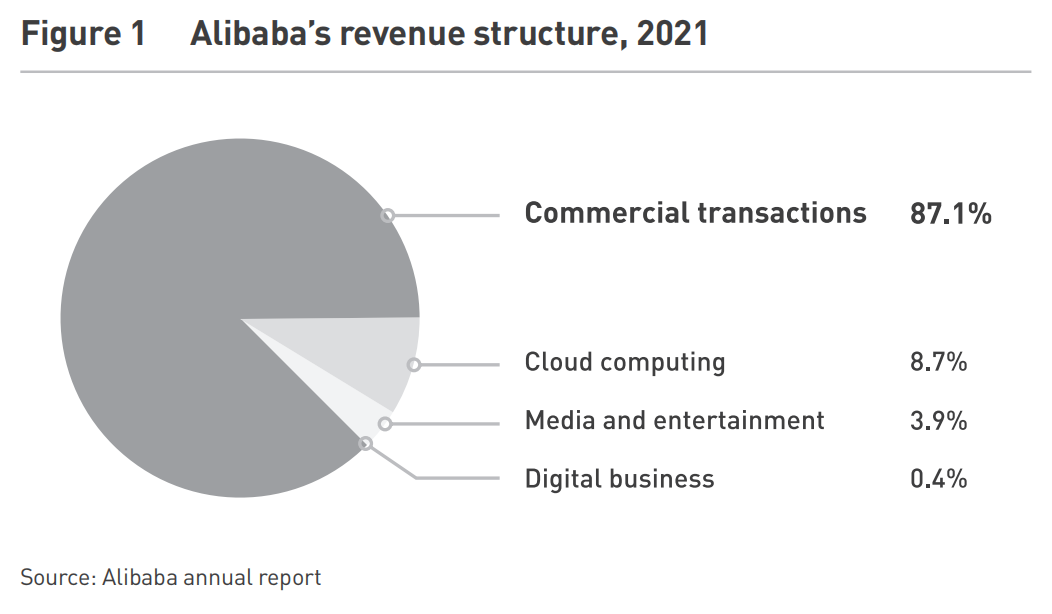
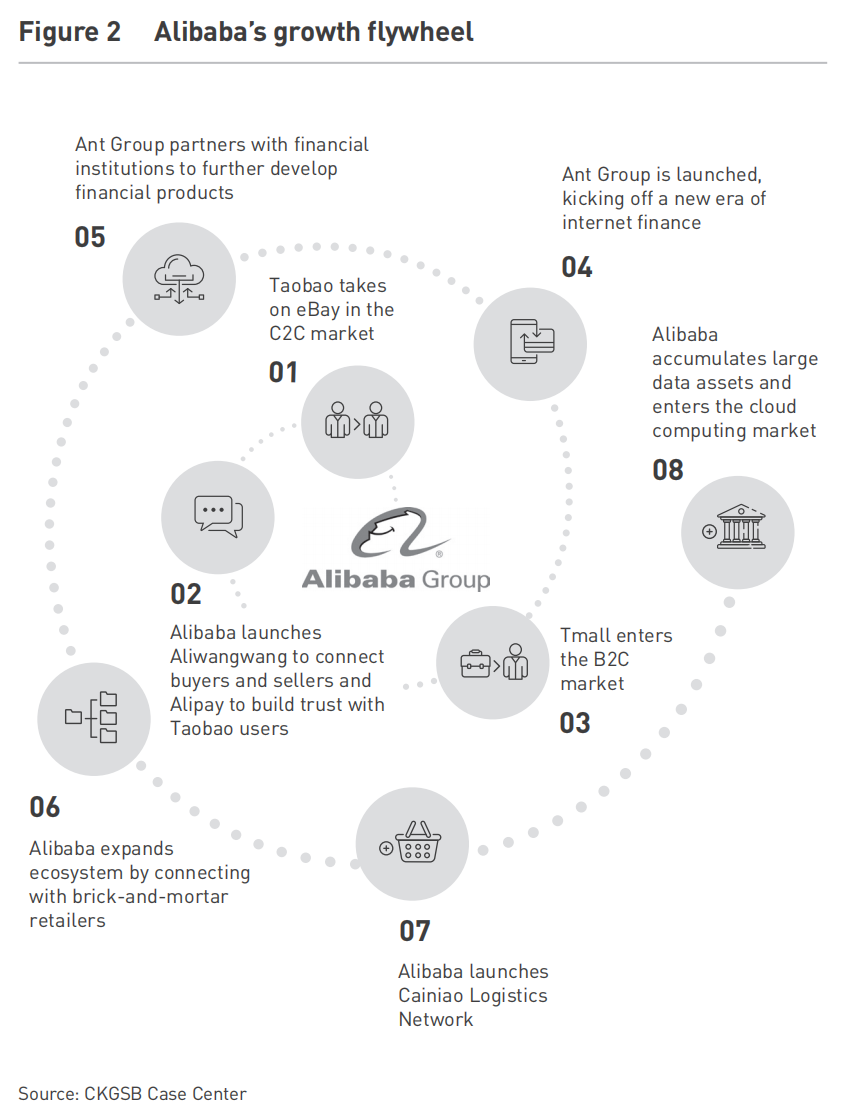
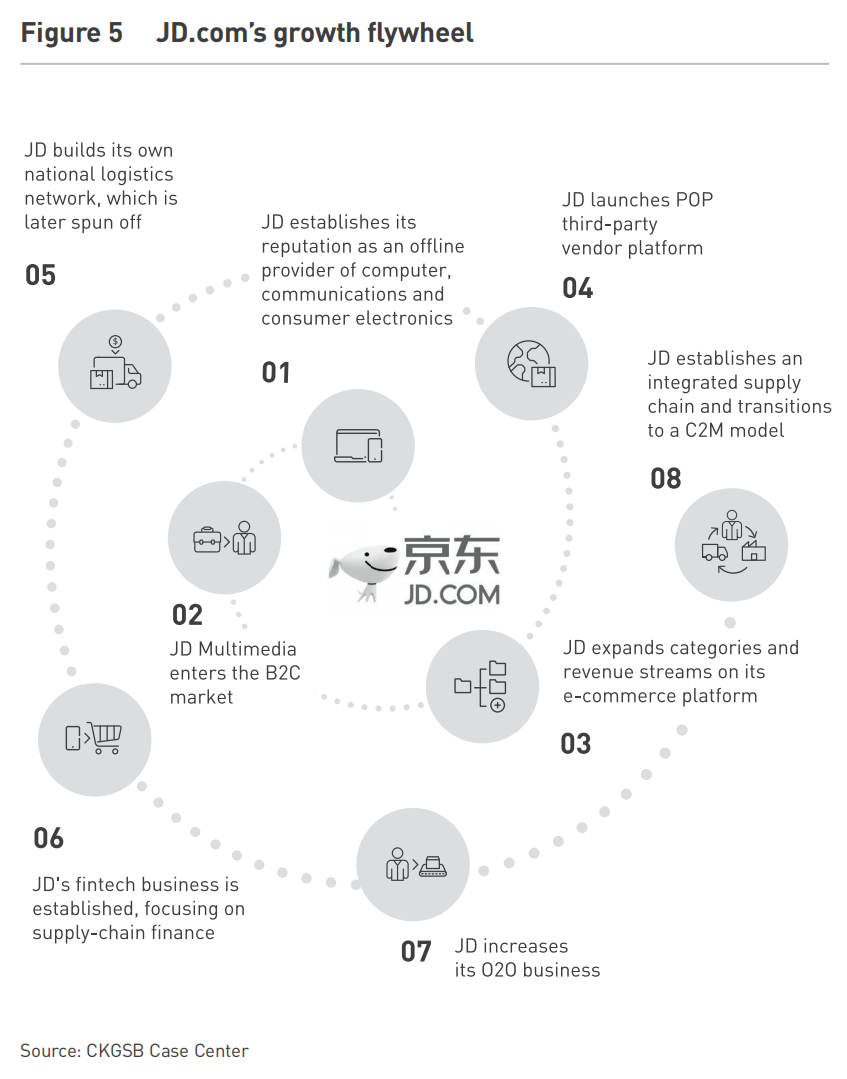
Alibaba and JD.com exemplify the “flywheel effect,” where small successes build accumulative momentum that propels sustained growth (see Figure 2). Alibaba’s journey began in 2003 with Taobao, which disrupted eBay’s presence in China, later expanding platforms like Tmall, AliExpress, and Cainiao Logistics, creating an ecosystem spanning retail, advertising, logistics, and cloud computing. By 2021, commercial transactions accounted for 87.1% of Alibaba’s revenue, largely driven by advertising and commissions (see Figure 1). On Singles’ Day 2021, Alibaba’s Tmall recorded a GMV of RMB 540 billion (USD 80 billion), an 8.5% YoY increase, while JD.com reached RMB 349 billion (USD 52 billion), a 28.6% YoY rise—strong growth despite mounting competition.
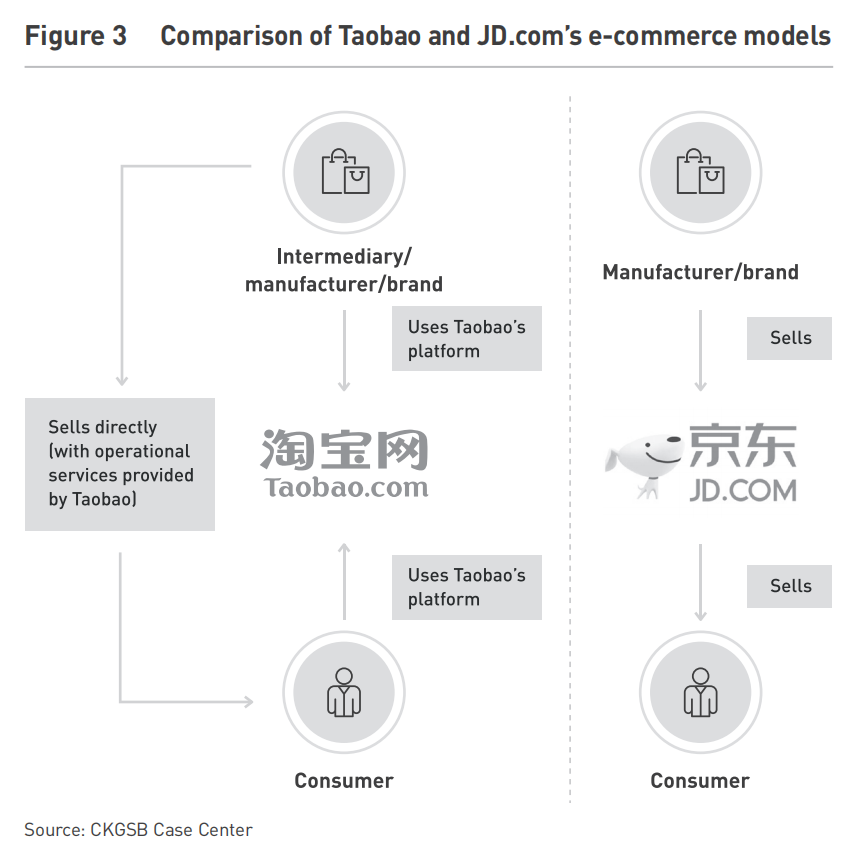
JD.com, on the other hand, adopted a merchant intermediary approach, prioritizing direct sales and meticulous control over its supply chain. By establishing its own logistics network in 2007, JD.com significantly improved delivery speed and quality control, reducing average inventory holding time from 50 days in 2011 to just 28 days by 2021. Despite JD.com’s 2021 revenue surpassing Alibaba’s by over RMB 100 billion (USD 15 billion), Alibaba maintained ten times JD.com’s net profit and twice as many active users. Today, 90% of JD.com’s revenue comes from its self-operated business, with third-party logistics and advertising making up the rest (see Figure 4).
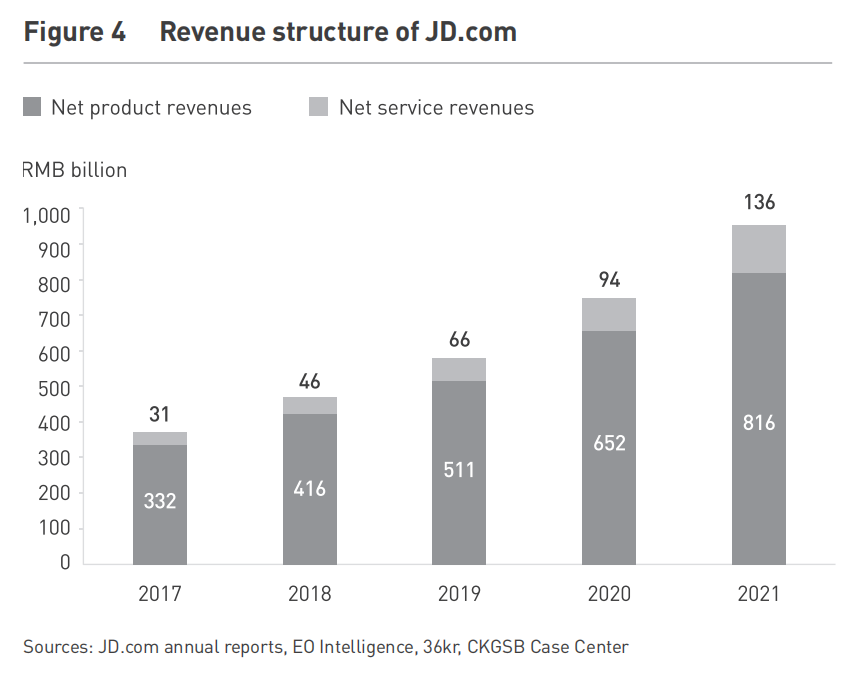
Note: JD.com’s revenue structure: the dark color represents revenue from its own brands and the light blue from services (Unit: 1000 = RMB 100 billion)
Alibaba: Restructuring for the Future
By 2005, Taobao’s annual revenue hit RMB 8 billion (USD 1.2 billion), surpassing Walmart China, and it became Asia’s largest online marketplace by transaction volume. In just four years, it amassed 30 million users, offering a diverse range of products by leveraging a long-tail strategy for specialized and hard-to-find goods. In 2004, Jack Ma introduced Aliwangwang to facilitate buyer-seller communication and launched Alipay, which improved transaction security by holding funds in escrow until buyers received their purchases.
In March 2023, Alibaba unveiled a major organizational overhaul to enhance agility and innovation. The company restructured into six independent business groups:
- Taobao and Tmall Group – Taobao, Tmall, Xianyu, 1688.com
- Alibaba International Digital Commerce Group – Lazada, AliExpress, Trendyol, Alibaba.com
- Local Services Group – “To-Home” services (Ele.me) and “To-Destination” services (Amap)
- Cainiao Network
- Cloud Intelligence Group – Alibaba Cloud, DingTalk, and other businesses
- Digital Media and Entertainment Group – Youku, Damai, Alibaba Pictures
This restructuring grants each group operational independence, promoting faster decision-making and a sharper focus on specific markets. It reflects Alibaba’s strategy to enhance globalization, boost domestic consumption, and capitalize on big data powered by cloud computing.
JD.com: IPOs and Streamlined Management
March 2023 also marked a significant milestone for JD.com, as two of its subsidiaries—JD Industrials and JD Property—filed for IPOs in Hong Kong. Both deals are estimated to exceed USD 1 billion, with JD.com retaining a controlling stake in these units. The IPOs reflect JD.com’s ambition to unlock value from its subsidiaries while reinforcing its core business dominance.
Meanwhile, JD.com has been streamlining its organizational structure. JD Retail and JD Logistics have adopted flatter management hierarchies, improving efficiency and responsiveness. This decentralization strategy is expected to extend across other business units, reinforcing cost reduction and operational excellence.
Competition and Innovation: Driving Growth
The rivalry between Alibaba and JD.com extends beyond market share—it represents two distinct business philosophies. Alibaba’s ecosystem-driven approach connects consumers and merchants through data and services, while JD.com’s vertically integrated model focuses on direct sales and supply chain control. However, both companies continue to innovate, as seen in their respective initiatives (see Figure 3 &5):
- Alibaba’s Cainiao Logistics collaborates with over 3,000 logistics partners, delivering 4 million packages daily worldwide.
- JD.com’s C2M (Consumer-to-Manufacturer) model leverages data analytics to optimize manufacturers optimize product design, as seen in its partnership with Midea Group to develop the popular “Vitamin C refrigerator.”
The Road Ahead
As China’s e-commerce market matures, both Alibaba and JD.com face slowing growth rates and heightened competition. However, the global retail market, valued at over USD 25 trillion, presents substantial opportunities for international expansion.
To sustain their lead, both companies must navigate regulatory scrutiny, price wars, and technological disruptions. Alibaba’s restructuring reflects its push for greater flexibility and innovation, while JD.com continues to prioritize supply chain efficiency and logistics expertise.
The rivalry between Alibaba and JD.com is more than just a competition—it’s a blueprint for how digital innovation and strategic pivots can redefine industries. As these e-commerce giants continue to evolve, their success will depend on their ability to balance growth, innovation, and resilience in an ever-changing global market.
This article is part of the “Unleashing Innovation in China” series, which explores how companies are driving innovation and reshaping industries in one of the world’s most dynamic markets. For more insights, visit: Unleashing Innovation: Ten Cases from China on Digital Strategy and Market Expansion – CKGSB Knowledge




















