Opinion By Dr. Ouyang Hui and Ye Dongyan
Dr. Ou-Yang Hui is the Dean’s Distinguished Chair Professor of Finance, Associate Dean for EMBA and a Professor of Economics at Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business
Ye Dongyan is a researcher at the Financial Innovation and Wealth Management Research Center at Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business
As China struggles to contain the spread of COVID-19, everyone is wondering how this incident will impact the greater economy. Although there are still many uncertainties about the current crisis, to compare the repercussions of this virus with the SARS virus, which broke out in 2003, is optimistic. Back then, China’s share of the world’s GDP was 8.8%; now it’s 19.2%. China’s economy grinding to a halt will have massive impacts around the world.
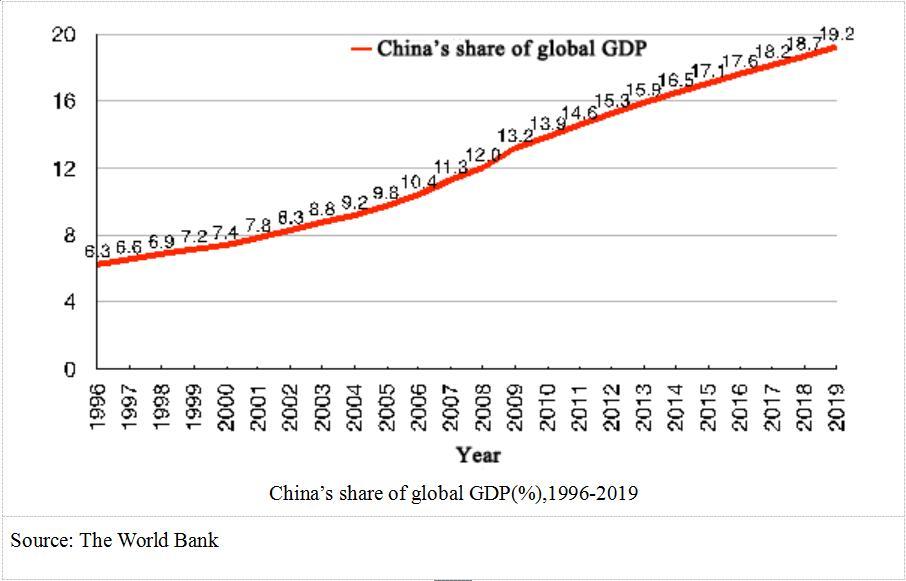
China’s growth rate and economic structure is very different now compared to 17 years ago. After SARS, China’s ended the year with a 10% GDP and an economy largely back on track roaring with full steam ahead. However, we are unlikely to see this type of recovery now. China’s economy has shifted down several gears from a manufacturing industry to a more service industry with a lower GDP in 2019 of 6.1% compared to 10.6% in 2010. The export to GDP ratio in 2003 was 26.4% so exports swiftly helped the country recover after SARS. However, in a post tariff-war climate, exports take on a smaller role in the economy, making China’s GDP target of 6% a hard goal to hit.
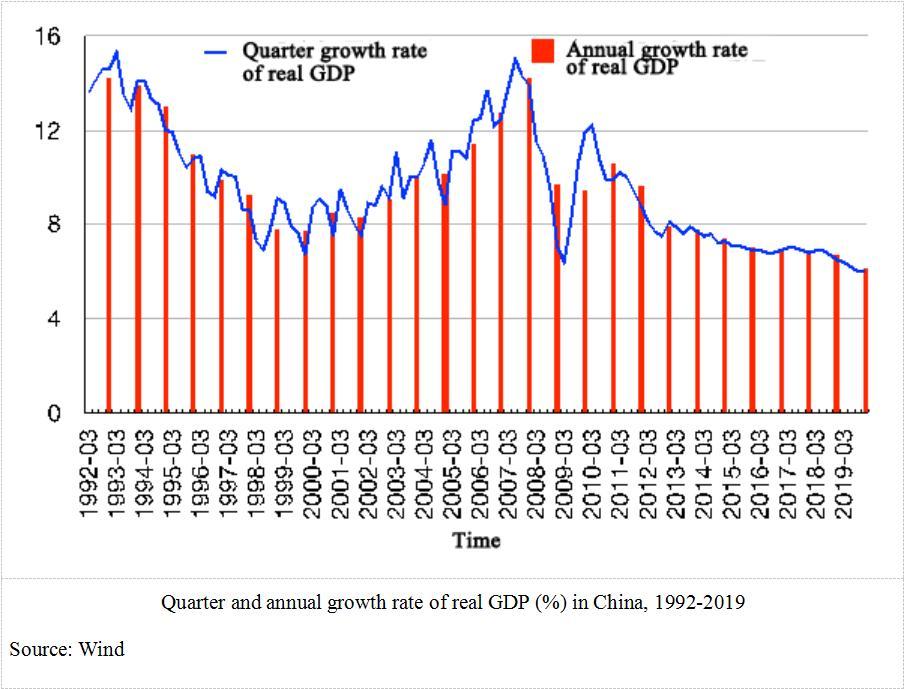
Economic activity has slumped since Lunar New Year, a festival that usually drives considerable growth in consumption and services, from tourism to entertainment. Moreover, workers have been trapped in their home after the holiday and prevented from returning to work for fear of the disease spreading further. This is something China has never experienced in the last 40 years of economic growth.
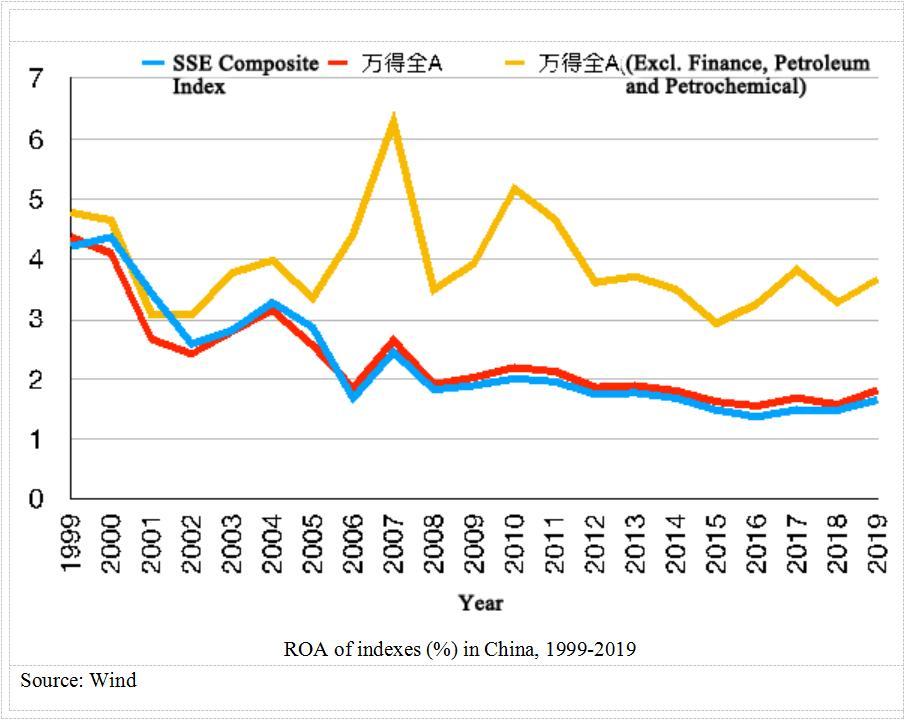
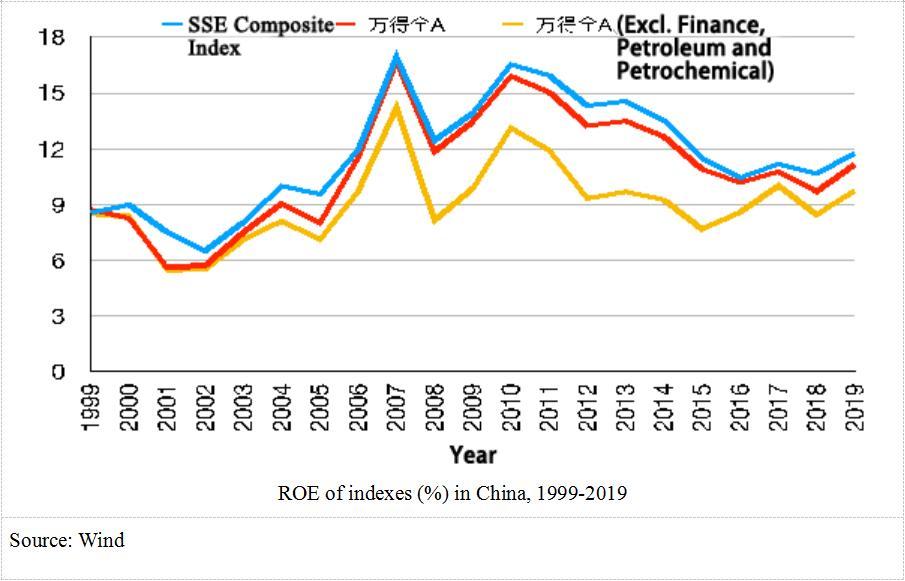
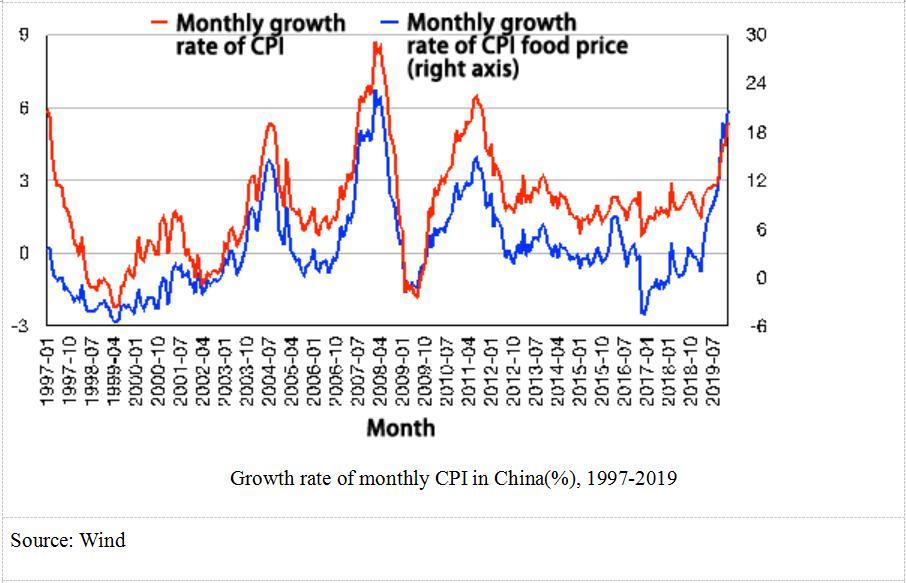
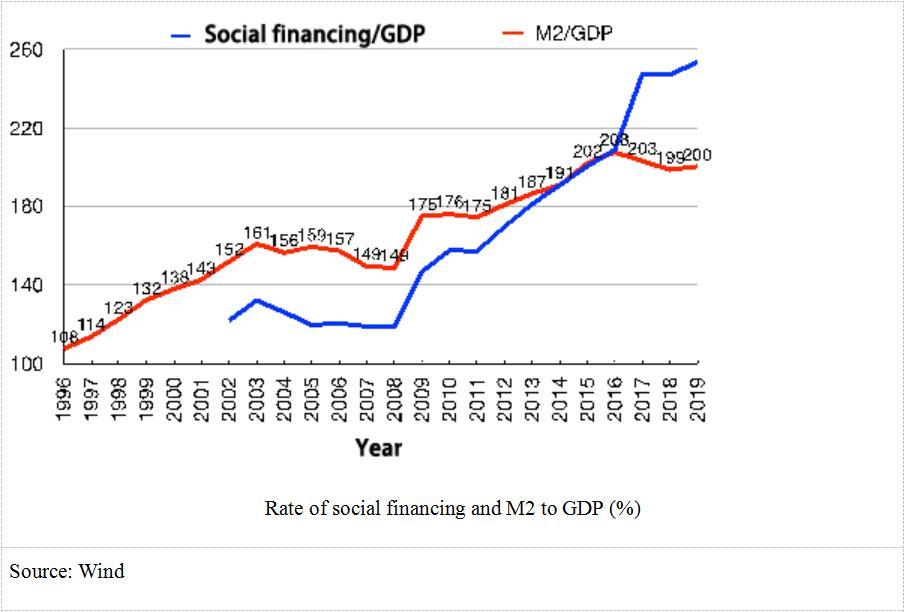
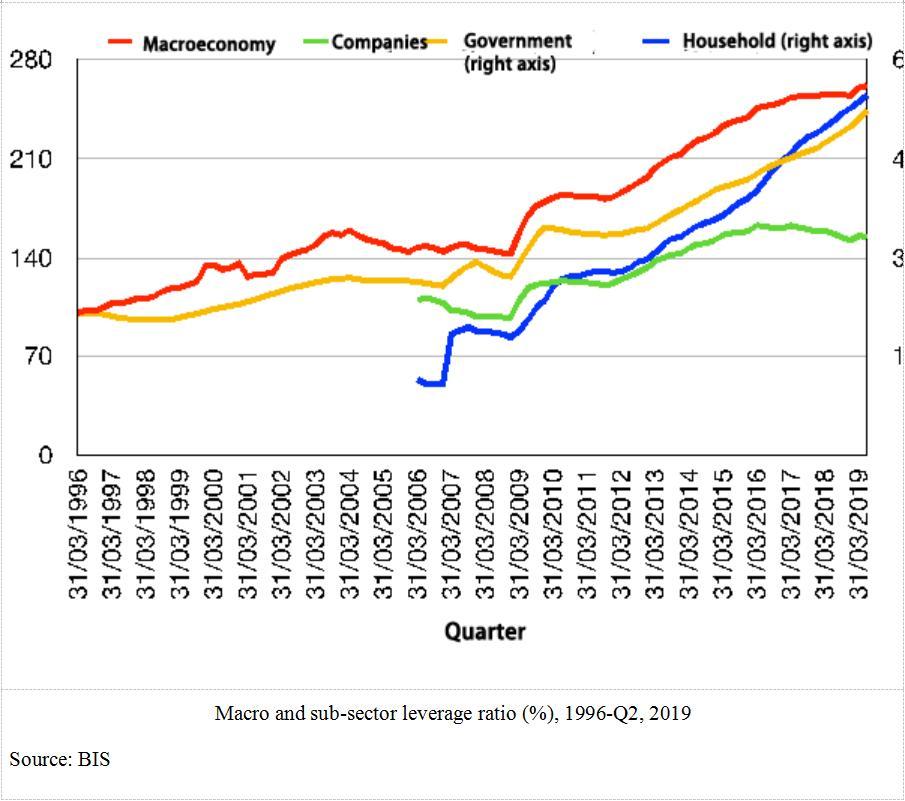
The profitability of companies during the SARS period was high and rising with industrial added value, ROA and ROE all high and rising, making it easier to recover from the crisis. Inflation was under 1% for most of 2003, compared to 5.4% inflation now. The food price index has risen as much as 20.6%. On top of this, companies and households are highly leveraged now than before. The M2 to GDP ratio was 161% in 2003 and 200% in 2019. Social financing to GDP has also grown from 132% in 2003 to 254% in 2019. Although there is limited room for maneuver, China can still cut benchmark interest rates even lower.
The government should urgently reduce taxes and expand investment in infrastructure, scientific research, environmental protection and healthcare, issue more money, cut interest rates, and protect equity markets. Stability of the stock markets can help reduce unbearable corporate leverage. Small and medium enterprises (SME) in particular need direct government support. Administrative fees should be suspended, and rent reduced or exempted. Tax rebates or deferred payments should be rolled out, as should subsidies for research and development.
COVID-19 will have a greater impact than SARS, and recovery will likely take longer. To support companies, especially SMEs, no effort or expense should be spared. The government will need to adopt a larger and broader stimulus package than it did during SARS and even during the global financial crisis in 2008. If not, companies will go bankrupt, and large-scale unemployment will follow. This public health crisis could lead to a financial, economic, or even political crisis that would have global implications.




















