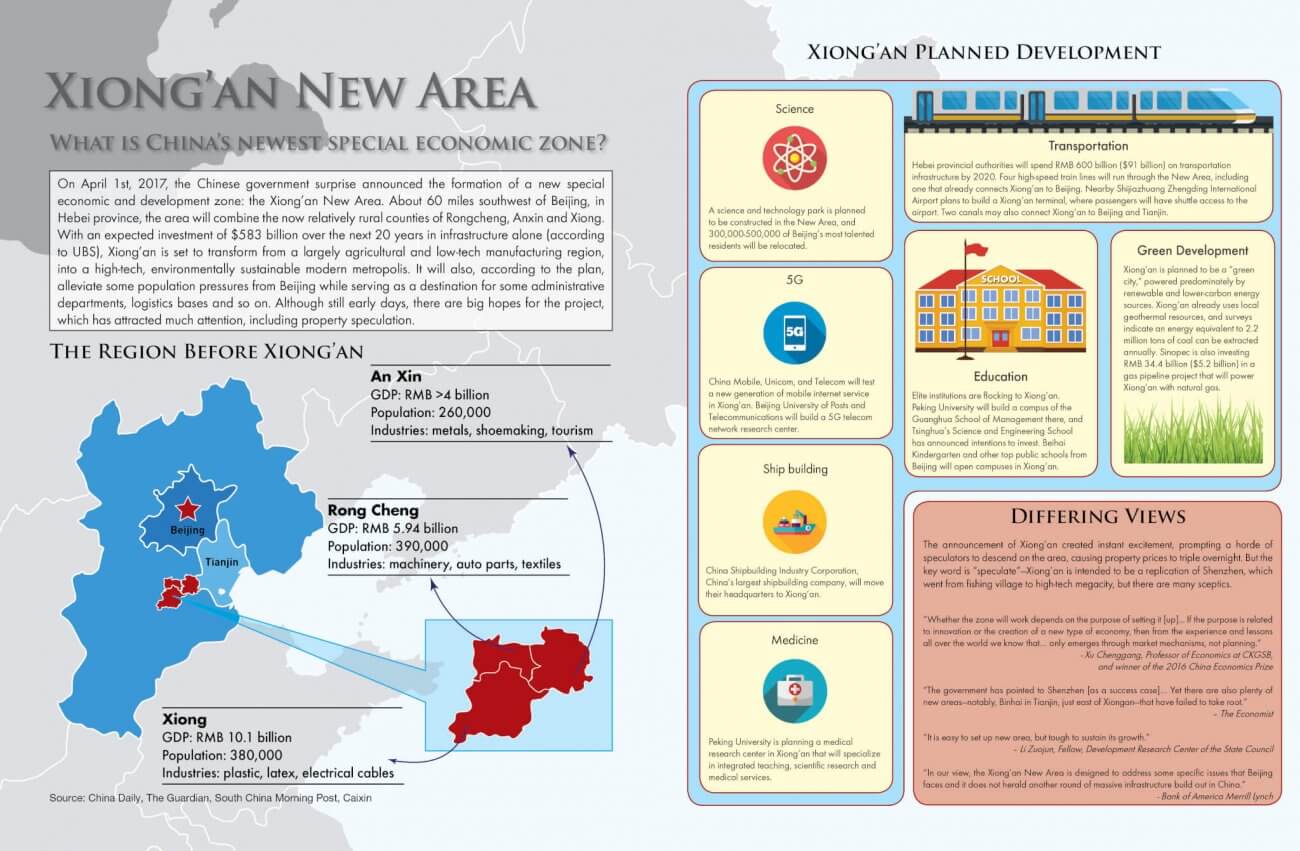
On April 1st, 2017, the Chinese government announced the formation of a new special economic and development zone: the Xiong’an New Area. About 60 miles southwest of Beijing, in Hebei province, the area will combine the now relatively rural counties of Rongcheng, Anxin and Xiong. With an expected investment of $583 billion over the next 20 years in infrastructure alone (according to UBS), Xiong’an is set to transform from a largely agricultural and low-tech manufacturing region, into a high-tech, environmentally sustainable modern metropolis. It will also, according to the plan, alleviate some population pressures from Beijing while serving as a destination for some administrative departments, logistics bases and so on. Although still early days, there are big hopes for the project, which has attracted much attention, including property speculation.
Xiong’an Planned Development
Science: A science and technology park is planned to be constructed in the New Area, and 300,000-500,000 of Beijing’s most talented residents will be relocated.
5G: China Mobile, Unicom, and Telecom will test a new generation of mobile internet service in Xiong’an. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications will build a 5G telecom network research center.
Ship building: China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation, China’s largest shipbuilding company, will move their headquarters to Xiong’an.
Medicine: Peking University is planning a medical research center in Xiong’an that will specialize in integrated teaching, scientific research and medical services.
Transportation: Hebei provincial authorities will spend RMB 600 billion ($91 billion) on transportation infrastructure by 2020. Four high-speed train lines will run through the New Area, including one that already connects Xiong’an to Beijing. Nearby Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport plans to build a Xiong’an terminal, where passengers will have shuttle access to the airport. Two canals may also connect Xiong’an to Beijing and Tianjin.
Green Development: Xiong’an is planned to be a “green city,” powered predominately by renewable and lower-carbon energy sources. Xiong’an already uses local geothermal resources, and surveys indicate an energy equivalent to 2.2 million tons of coal can be extracted annually. Sinopec is also investing RMB 34.4 billion ($5.2 billion) in a gas pipeline project that will power Xiong’an with natural gas.
Education: Elite institutions are flocking to Xiong’an. Peking University will build a campus of the Guanghua School of Management there, and Tsinghua’s Science and Engineering School has announced intentions to invest. Beihai Kindergarten and other top public schools from Beijing will open campuses in Xiong’an.